Global R+D trends in Surgical Robotics
- Edu Soler
- no comments
Something is changing in the surgery market. Surgical robots are further more than the Da Vinci System. Two key trends are driving the new surgical era: 1) New companies entrance, 2) Increase in the number of indications and procedures.
This report focuses on most relevant robotic surgical systems in the market as well their entry barriers, trends, market size, most relevant institutions and others.
Robotic surgery was developed to try to overcome the limitations of pre-existing minimally-invasive surgical procedures and to enhance the capabilities of surgeons performing open surgery.
This table resumes the top 9 surgical robots in the market.
| Device | Purpose | FDA aproved | Company | Country |
| Da Vinci | urolo, general, laparo, gyne, thora, cardio | YES | Intuitive Surgical | US |
| Senhance | laparo, gyne | YES | TransEnterix | US |
| NAVIO | orthope, neuro | YES | Smith & Nephew | US |
| Mazor X | orthope, spine, neuro | YES | Medtronic | US |
| MAKO | orthope, knee | YES | Stryker | US |
| Monarch ARES | bronco, lung cancer | YES | Johnson & Johnson | US |
| Versius Surgical | gyne, colon, renal | NO | CRM Surgical | ENG |
| Flex Robotic | transoral | YES | Medrobotics | US |
| SPORT | urolo, general, gyne, colon | NO | Titan Medical | US |
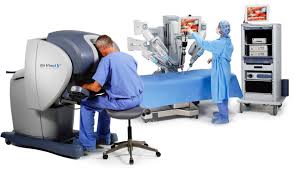
TOP 1. The Da Vinci system (S, Si, X, Xi, SP)
Product description: consists of ergonomic surgeon console, patient-side cart with interactive arms, vision system, and proprietary instruments/accessories like the EndoWrist that provides an additional seven DOF by mimicking the movements of the human wrist.
Company: Intuitive Surgical has remained the main powerhouse within robotic surgical systems. It’s primarily located within the US, even though a rapid growth is seen within the EU and APAC regions (Asia-Pacific).
Differentiation value: largest adoption in the market, multi-specialty surgical platform.
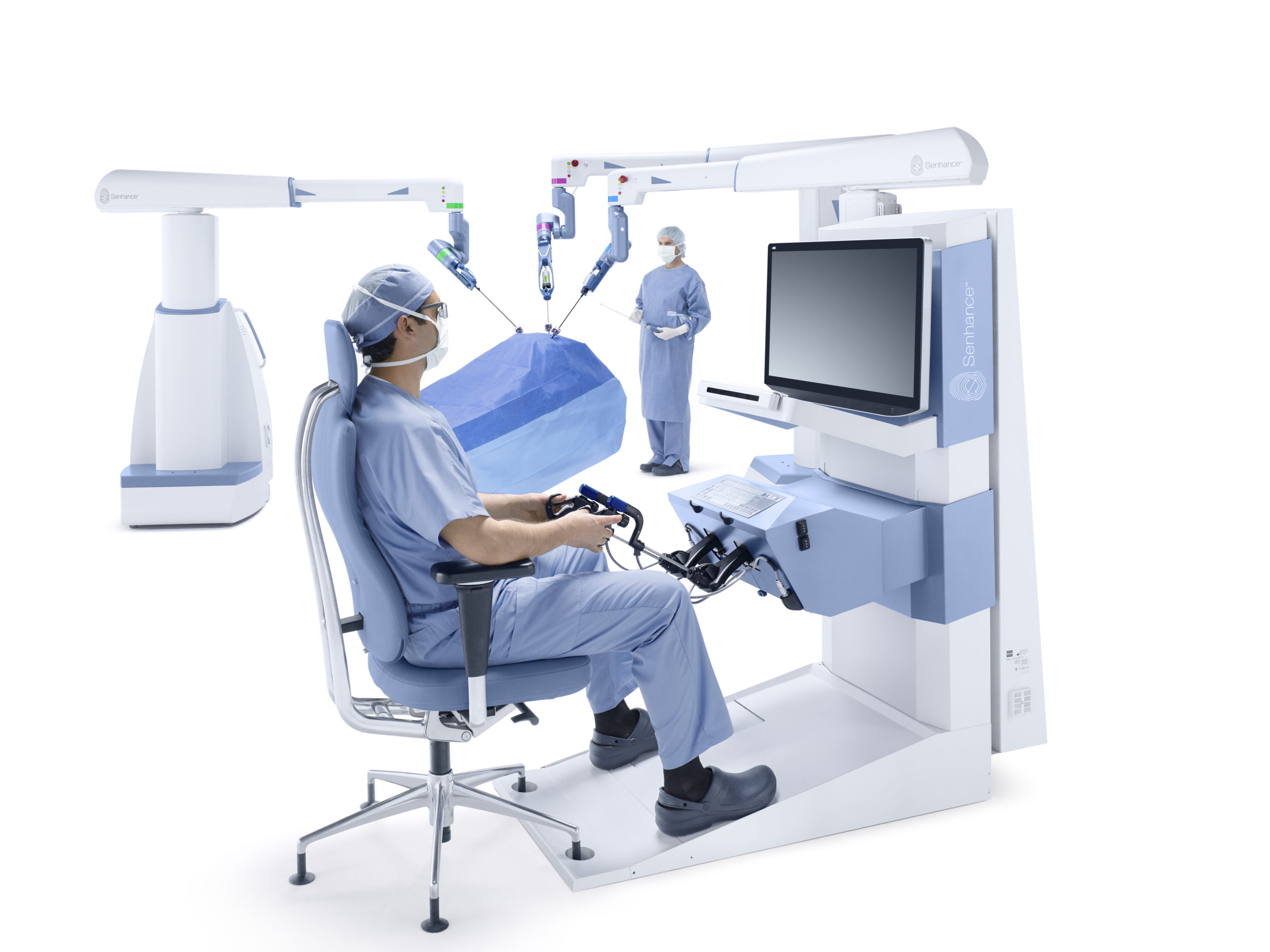
TOP 2. Senhance System
Product description: Senhance is a console type robotic platform consisting of a remote control station unit, manipulator arms, and a connection node. The robot system comprises three arms, each individually mounted on its own cart.
Company: TransEnterix has a higher installed base within the EU than within North America. The company has also been receiving steady approvals in major regions such as APAC.
Differentiation value: utilize already installed capital equipment, Instrumentation is fully reusable, gauge tissue response.
TOP 3. NAVIO
Product description: NAVIO System directly target the orthopaedic market. It provides real time imaging allowing the system to be CT-free. The handheld maneuverability allows for precise implants to be placed within patients.
Company: Smith & Nephew is one of the biggest orthopaedic multinationals companies. The overall strategy is to lead to an automated robotic surgical environment which they are currently working on.
Differentiation value: orthopedic oriented, personalized approach to the implant.
TOP 4. Mazor X
Product description: The Mazor X is indicated for precise positioning of surgical instruments or spinal implants during general spinal and brain surgery. It may be used in either open or minimally invasive or percutaneous procedures.
Company: Medtronic has been positioning itself to become a competitor within the robotic surgical space. Through acquisitions and partnering Medtronic has launched the Mazor X Stealth robotic-assisted spinal surgical platform.
Differentiation value: orthopaedic and neurosurgery oriented, high software development.
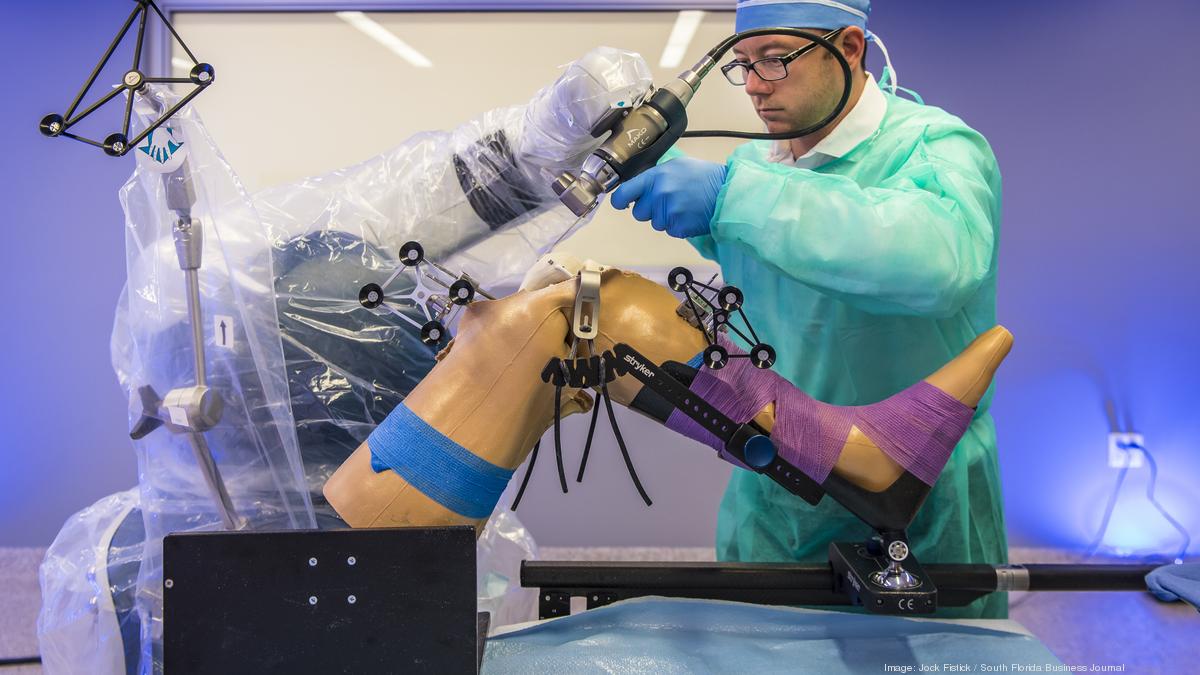
TOP 5. MAKO
Product description: The system allows for precise and accurate implants and makes Mazor X a major player in total knee and total hip replacement robotic procedures.
Company: Stryker is the market leader within the knee and hip robotic surgical market, and will continue to dominate the US market in the coming years within the segment.
Differentiation value: orthopaedic oriented, specifically partial and total knee replacement, preoperative planning.
TOP 6. Monarch system or ARES
Product description: Monarch is a teleoperated endoluminal bronchoscope designed to clarify the bronchoscope with articulated tip can be attached at the end effector of the arm, and the design allows an endoscopist to bend the bronchoscope in four directions.
Company: Johnson & Johnson purchased Auris Health Inc who has the Monarch system, the first FDA cancer-approved robot on the market.
Differentiation value: lung cancer diagnosis and therapeutics.
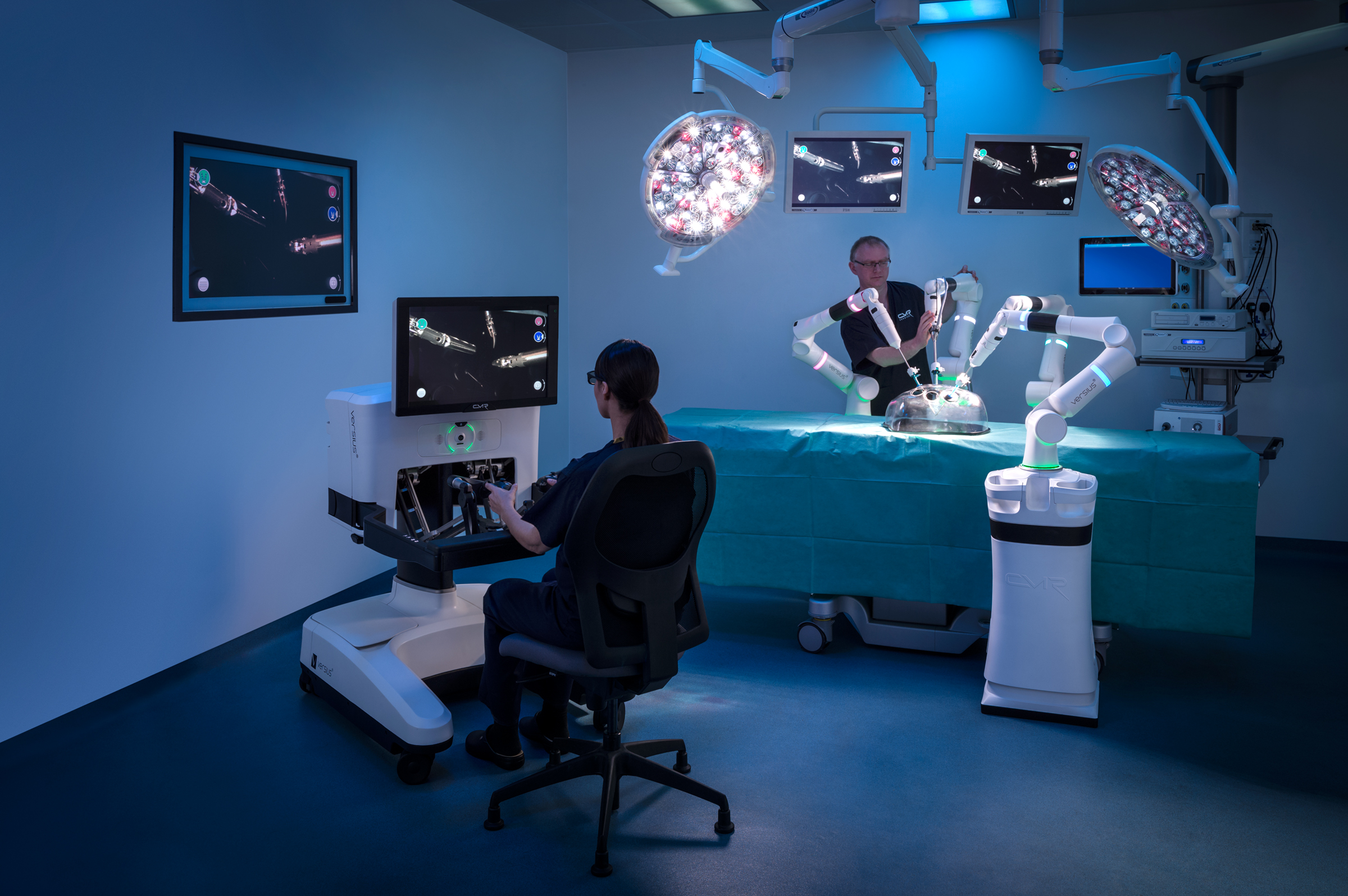
TOP 7. Versius Surgical
Product description: The Versius Surgical Robotic System aims to make minimal access surgery easier for surgeons. The system can use up to five individual arms, each with its own base.
Company: The Versius Surgical Robotic System is anticipated to be priced lower than the average price of da Vinci systems. This is expected to offer surgeons a more cost effective option.
Differentiation value: portable, transportable and affordable.
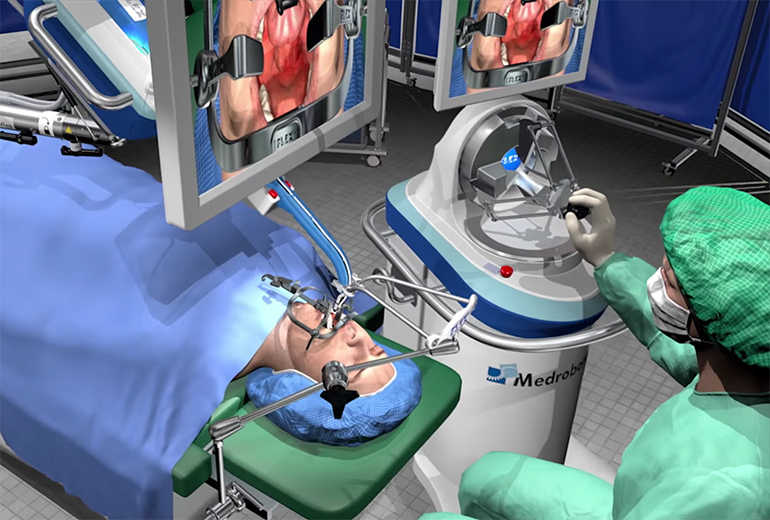
TOP 8. Flex Robotic System
Product description: The Flex Robotic System is a minimally invasive robotic surgical system which provides access to the complex anatomical sites. The Flex Robotic System it can navigate an approximately 180 degree paths to reach inaccessible surgical targets.
Company: Medrobotics S.L. vision to offer patients surgical options that are carried out through natural body orifices places them in a competitive position within the space.
Differentiation value: portable, natural body orifices.
TOP 9. SPORT Surgical System
Product description: The SPORT Surgical System is a versatile single-incision advanced robotic surgical system that features multi-articulated instruments with 3D high definition visualization on a flat-screen monitor. The system is equipped with a single-arm mobile patient cart for ease of set up.
Company: Titan Medical lost nearly half its value in October 2019 after suspending the timeline for bringing the device to market due to lack of funds. In November, the company put its research and development work on hold while it looked for funding.
Differentiation value: portable, urology.

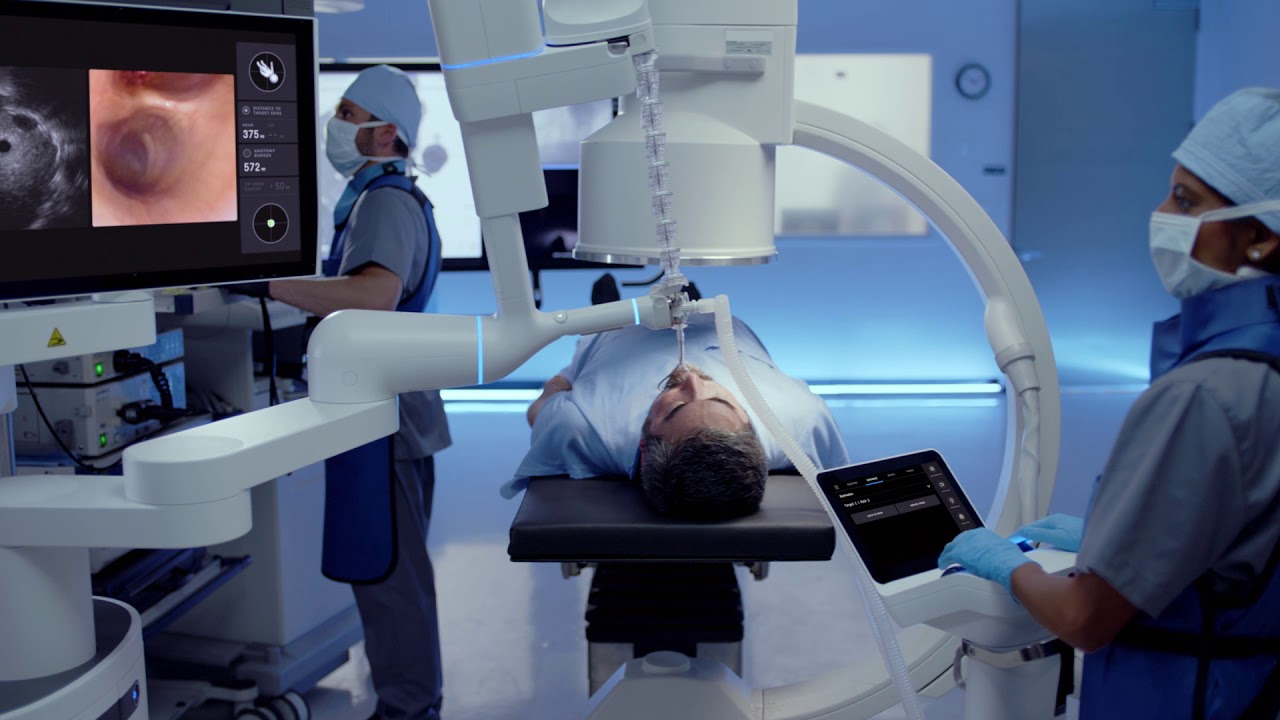
Ion
A robotic endoluminal system, designed to let surgeons perform minimally invasive biopsies deep in the lung. FDA approved by Intuitive Surgical.
web
Miniature in vivo robot (MIVR)
Miniature in vivo robot (MIVR) is a miniaturization of robotic arms and the motors that drive them, which allows for a reduced footprint and greater access to the patient relative to conventionally sized robots.
web
Surgibot
A single-port system to enhance laparoscopic procedures. FDA approved and commercialized by TransEnterix in USA and GIBL in China.
web
Sensei X
The Sensei X robotic catheter system is a cardiac catheter insertion. FDA approved by Hansen Medical Inc.
web
Preceyes
A robotic assistant for eye surgery. The system provides surgeons with a precision better than 20 μm to position and hold instruments. This high surgical precision aims to improve treatment outcomes and empowers surgeons to establish new innovative surgical techniques, including delivery of advanced therapeutics. CE mark approved.
web
FreeHand v1.2
FreeHand 1.2 is a robotic camera controller developed for minimally invasive surgery that enables the user to control the camera handsfree. FDA approved by FreeHand 2010 Ltd.
web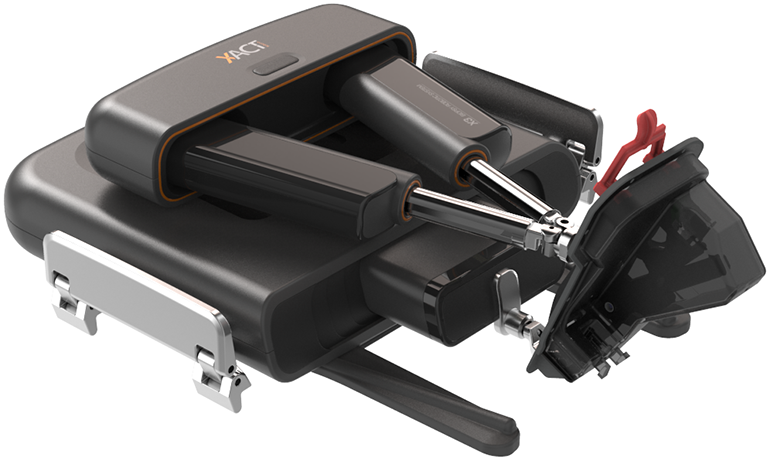
XACT Robotics
A hands-free robotic system that combines image-based planning and navigation with insertion and steering of various instruments to a desired target during percutaneous procedures. FDA and CE mark approved.
web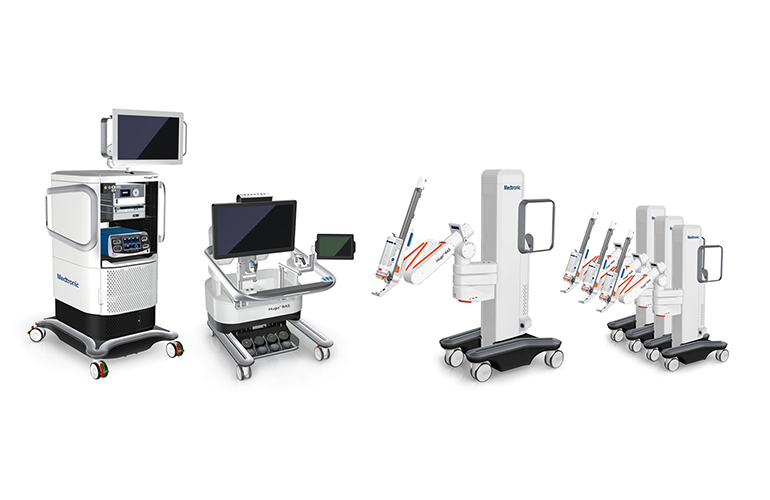
Hugo
Medtronic’s investigational robot-assisted surgery system includes a tower, surgeon console, surgical end effectors, and robotic arm carts. The system is advertised to be flexible with a wide range of uses in bariatric, thoracic, colorectal, general, and urologic surgeries.
web
MiroSurge
A tele manipulated minimally invasive robotic surgery system. It has individual minimally invasive robot-assisted arms carrying an instrument can be mounted to the bed rails at various locations.
web
ViaCath system
A steerable flexible diagnostic catheter. It is a teleoperated endoscopic robot, composed of a master console and slave with long-shafted instruments that run along a standard colonoscope or endoscope.
web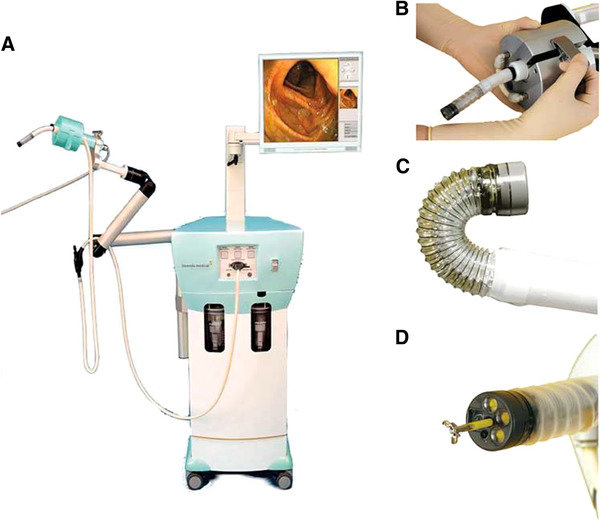
Invendoscopy E200 system
The invendoscopy E200 system is composed of a reusable handheld controller and processing unit, as well as a single-use sterile. FDA approved by Invendo Medical GmbH.
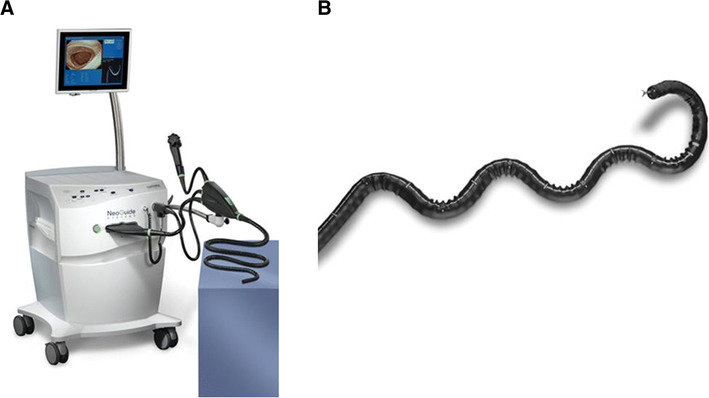
NeoGuide Endoscopy System
NeoGuide Endoscopy System is a computer-aided colonoscope that utilizes computerized mapping to travel along the natural curves of the colon, resulting in less force applied to the walls of the organ. FDA approved by NeoGuide Endoscopy System Inc.
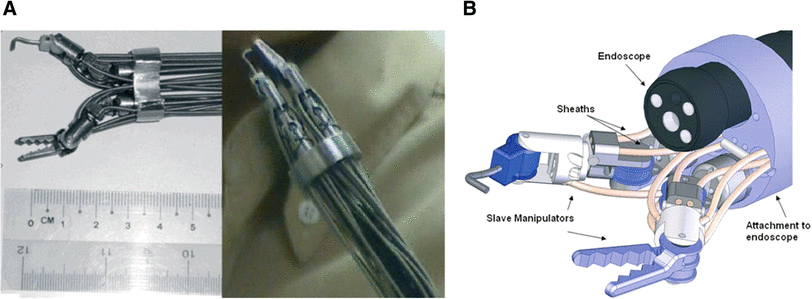
MASTER
A multidimensional robotic device for NOTES. The platform allows bimanual steering of two arms, provides dexterity, triangulation, haptic feedback to maintain spatial orientation, and a navigation system that allows a three-dimensional reconstruction that can be utilized to manoeuvre in real time.
Since the launch of the first Da Vinci System in 2.000, robotic surgery adoption has been less that it was expected. Many barriers have stopped hospitals to incorporate this modern technology. The following chapter describe briefly some actual ones.
1. Continued development of skills set for surgeons
Integrating surgical robotic technologies into practice is strongly influenced by adequate training of all team members and previous experience with robotic platforms.
2. Limited reimbursement
Reimbursement to hospitals and surgeons for surgical procedures can act as a significant booster for the uptake of products utilized during the surgery. If hospitals and surgeons receive the same reimbursement irrespective of the products that are used in the procedure, this will act as a hurdle for adoption.
3. Limitations with currently available robots
Limitations within general surgery include a large footprint (size) and lack of haptic feedback. Newer products expected to be launched are anticipated to address these limitations.
4. Lack of sufficient clinical trial studies
As with all new devices, more number of clinical studies is required to establish the clinical and cost-effectiveness of robotic surgical systems. Although the initial uptake of these systems in many regions have been positive, it is obvious that the full potential of these systems in a surgical setting has not been realized to its maximum specially in the cost-effectiveness.
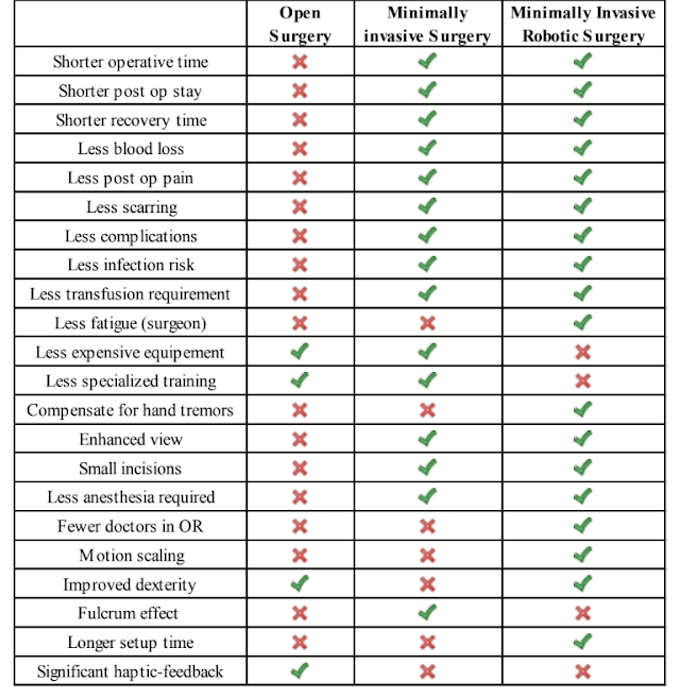
In the following table we have a comparison resume between Open surgery, Minimally Invasive Surgery and Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery.
Source: Robotic Surgery - A Review on Recent advances in Surgical Robotic Systems. J Dwivedi. I Mahgoub.Following the data of the consulting company Global Data, the robotic surgical systems market for general surgery, excluding accessories, was estimated at $778.5M in 2017 and by 2024 it estimates a market of $1,890.6M. This industry is specially growing comparing to other healthcare sectors. Next table describes the Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) by 2024 in different health tech sectors. As is shown, robotic surgery market is one of the most attractive sectors.
|
Health Tech Sector |
CARG |
|
Digital health devices |
29,6% |
|
Robotic surgery |
13,5% |
|
Home healthcare devices |
7,9% |
|
Diabetes devices |
7,8% |
|
Hemodialysis devices |
4,2% |
|
Cardiology drugs |
3,8% |
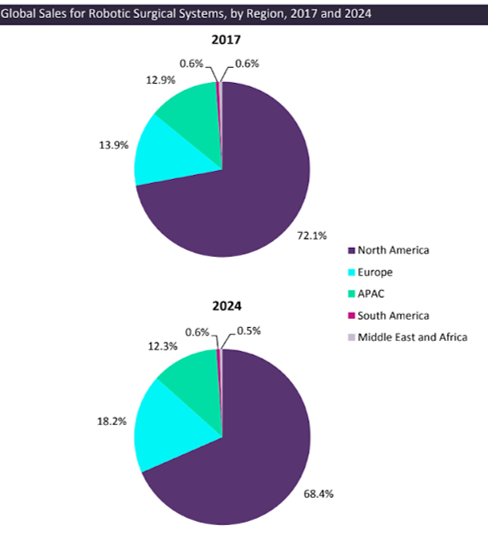
North America represents the majority of the sales worldwide, 70%. Europe represents 15% of it and is expected to grow when North America is expected to maintain. This growth can be attributed two main drivers: 1) Increase in the adoption and number of indications, and 2) Increase in number of companies with their own products.
Source: GlobalData MediPoint Robotic Surgical Systems Global Analysis and Market Forecasts 2018Major manufacturers are increasing their R&D efforts within robotic surgical systems. Intuitive Surgical, with the Da Vinci System, is the market leader, and its global procedures increased by 32% from 2017 to 2018. The entrance of major manufacturers such as Johnson & Johnson and Medtronic are bolstering the medtech surgical robotics market.
Each company tries to highlight its own features like; medical indication, number of consumables, size (foot print), surgery versatility and required training will be some of key differentiation values between robots.
Recently, there have been major movements within the robotics surgical systems. Smaller manufacturers are focusing on technological advances within these systems, while major manufacturers are focusing on acquiring already established surgical systems.
Initial patents allowed Intuitive Surgical a colossal head start over their competition. Intuitive Surgical has filed and had published nearly four times as many patent families in the last five years than in the five years between 2004 and 2009. However, patents have a maximum term of 20 years, and the protection provided by Intuitive’ original patent portfolio has started to expire.
Patent leaders

Intuitive surgical (US)
Ethicon Endo Surgery (US)

Corindus (US)

Samsung (Korea)

Omni (US)
The application of machine learning to surgical robotic systems appears to be a frontier in the robotic surgical intellectual property space. It’s not an entirely open frontier. This predictive robotic surgery capability is clearly an area to watch for developments coming both from Verb Surgical (Google) and from the significant others.
Because of the multitude of technical areas involved in surgical robotics massive number of universities are working in the field. This is small representation among the total assignees universities. Highlight the strong showing by the University of Nebraska from the efforts of Drs. Dmitry Oleynikov and Shane Farritor who lead a robotics-focused effort there, and who also are co-founders of Virtual Incision.
Universities leaders

Johns Hopkins University (US)

Massachusetts Institute of Technology (US)

University of Nebraska (US)

Columbia University (US)

Ecole Polytechnique (Switzerland)
Source: https://www.mddionline.com/overview-robotic-surgery-patent-landscape
Evolution is a continuous process and the surgical techniques are constantly being modified. The advent of Laparoscopy or Minimal Access Surgery was a boon to many patients giving them early recovery. Robotically assisted surgery was developed to overcome the pre existing limitations of Minimal Access Surgery i.e. 2D vision, dexterity, tremors, freedom and rotation of movements, surgical precision and accuracy and to enhance the capabilities of surgeons performing open surgery.
Future advances of robotic surgeries will be towards incorporation of all patient data like ultrasound, CT, MRI, etc. into robotic system to create a “virtual patient” and rehearse the surgery on virtual patient before actual surgery. Development of real time high speed data transfer technology will allow for Telerobotic Surgery.
Development of newer instruments and mass production of instruments may lower the cost of robotic procedures and will make it more affordable for a common man.
Source: Robotic surgery: Evolution, current status & future perspectives. Murtaza Akhtar, Divish Saxena.
R+D Surgical Robots CHRONOLOGY
- 1992: ROBODOC has the first surgical robot with FDA aprovance.
- 1994: AESOP 3000 is FDA approved for laparoscopic surgery.
- 1998: Dr. Friedrich Wilhelm developed an endoscopic camera.
- 2000: Da Vinci System is FDA approved.
- 2001: ZEUS robotic was FDA approved.
- 2002: SOCRATES developed for remote telesurgery.
- 2003: Merge of Da Vinci System and ZEUS.
- 2007: SENSEI is FDA approved.
- 2008: Mirosurge is developed in Germany.
- 2010: SOFIE a robot with force feedback.
Source: Surgical robotics: Reviewing the past, analysing the present, imagining the future. Paula Gomes.2011.
The Bitrack System
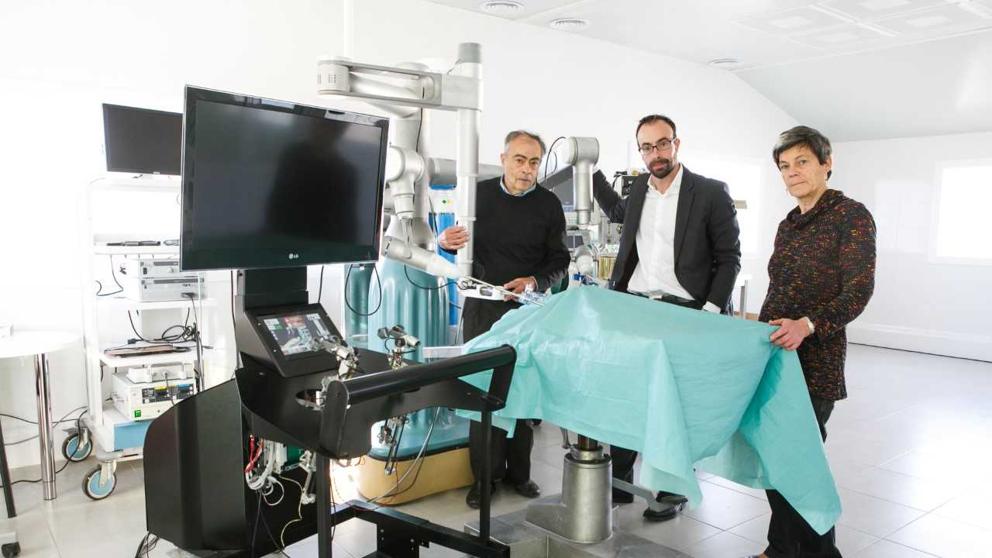

The bitrack System will be an alternative to the current laparoscopy surgical robot Da Vinci and will be an improvement on what is currently available in terms of efficiency.
It incorporates a flexible, modular and open robotic platform that improve the effectiveness of today’s robotic surgery and make it accessible to more hospitals around the world. It combines manual and robotic surgery, what is call hybrid minimally invasive surgery (HMIS).
The new robot has already been technically validated in experimental models, used by surgeons from the Mayo Clinic (United States) and the Barcelona university hospitals Clinic, Vall d’Hebron and Germans Trias. Between 2019 and 2021 Rob Surgical will build three new units to finalize the validation and industrialization process to expand the corporate and engineering team and will conduct the final safety and functionality trials.
Rob Surgical, the spin-off created by the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) and the Polytechnic University of Catalonia (UPC) in 2012, has closed a €5 million investment round with the Dutch holding Scranton Enterprises to fund the final phase of the new Bitrack System and launch the product onto the market.
Edu Soler
Science, healthcare and business are the three pillars that drive me nowadays. I love to engage new people in the adventure of healthcare innovation and always keep on learning from them. I am highly motivated with my participation in performing teams worldwide.
All stories by: Edu Soler